Adaptive streaming or Adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) refers to a process of encoding a single video file into multiple outputs with different bitrates and resolutions, which is delivered adaptively to target devices based on the playback CPU and connection bandwidth.
It is an essential tool used to improve the performance of video delivery and optimise user experience across different platforms and changing bandwidth conditions.
Adaptive Streaming has 4 major implementations:
- MPEG-DASH: Developed by MPEG, it is the only implementation that bears the ISO (International Standard). It enables streaming of media over the internet delivered from conventional HTTP web servers.
- Adobe Dynamic HTTP Delivery: Developed by Adobe, it delivers Adaptive Streaming to users by dynamically switching among varying streams during playback depending on size and quality.
- Apple HTTP Live Streaming: This protocol was implemented by Apple Inc. and it works by breaking down streams or video assets into several small MPEG-TS files of different bitrates using a Segmenter to ensure adaptive streaming.
- Microsoft Smooth Streaming: The Microsoft Smooth Streaming was developed by Microsoft that uses the ISS Media Services extension for Adaptive Streaming. The format for the Microsoft Smooth Streaming is based on the ISO base media file format.
 |
| Figure 1 - Illustration of Progressive Streaming (Source: Bitmovin Inc., 2019) |
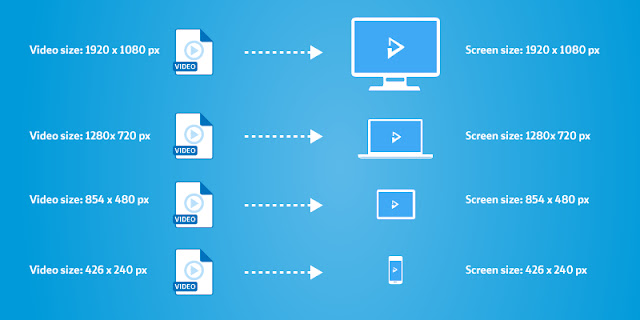 |
| Figure 2 - Illustration of Adaptive Streaming (Source: Bitmovin Inc., 2019) |
Looking at Figure 1, it can be seen that only one rendition of the media file was severed and accessed by various users regardless of their devices. The result during playback will include different issues ranging from poor video quality and lengthy buffering times.
Figure 2 depicts an ABR scenario where multiple versions of the same media files were encoded at different bitrate and resolutions and depending on the target device, the appropriate rendition will be served. This will result in smooth user experience.




Post a Comment